Blocks Area
Math
➗ Math – Your “Magic Calculator”
What it is: Blocks for doing math and calculations.
What it does: Performs operations with numbers.
Example: Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, dividing time, calculating distances.
👉 It’s the robot’s internal calculator
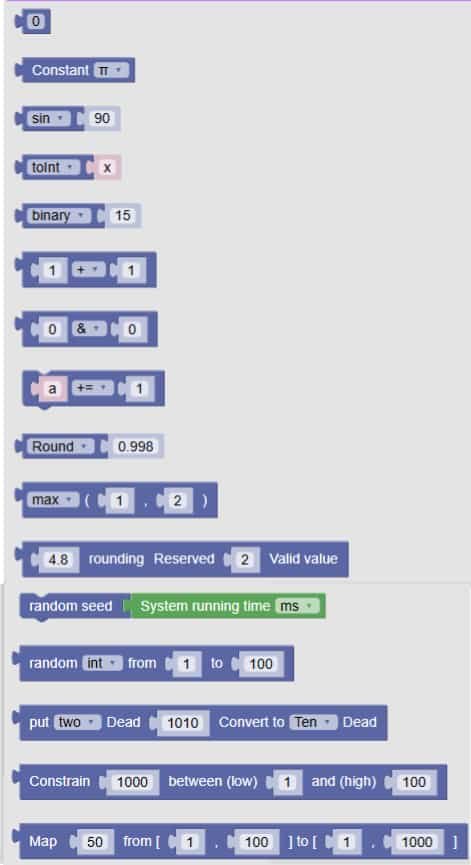
🧩 Fun Guide to Math Blocks (Clu-blocks Pro)
🧠 Important! Math blocks help your robot think with numbers — from simple addition to random values and even converting between number systems. They’re like your robot’s built-in calculator and logic engine!
| # | Block | What it does | Dropdown options | What the options mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 |
A number block | — | You can type any number here to use in your code |
| 2 | Constant π |
Inserts a math constant | π, e |
– π = 3.14159… (used in circles)– e = 2.718… (used in growth and logs) |
| 3 | sin 90 |
Applies a math function to a number | sin, cos, tan, asin, acos, atan, ln, log10, e^, 10^ |
These are trig and log functions — great for advanced math and angles |
| 4 | toint x |
Converts a value to another type | toInt, toFloat, transfer byte, bytetolnt |
– toInt: makes it a whole number– toFloat: makes it a decimal– Others are for byte conversions |
| 5 | binary 15 |
Converts a number to another format | binary, octal, hex |
Shows the number in binary (0s and 1s), octal, or hexadecimal |
| 6 | 0 ÷ 0, 0 ÷ 1, a ÷ 1 |
Division blocks | +, −, ×, ÷, %, //, ** |
– +: add– −: subtract– ×: multiply– ÷: divide– %: remainder– //: whole number division– **: power |
| 7 | Round: 0.998 |
Rounds a number | Round, Ceil, Floor, abs, sqrt |
– Round: nearest whole– Ceil: round up– Floor: round down– abs: absolute value– sqrt: square root |
| 8 | max(1, 2) |
Finds the biggest or smallest number | max, min |
– max: biggest– min: smallest |
| 9 | random seed System running time ms |
Sets the seed for random numbers | — | Makes random numbers more predictable (used in games or testing) |
| 10 | random int from 1 to 100 |
Generates a random number | int, float |
– int: whole number– float: decimal number |
| 11 | Random 100 between (low) 1 and (high) 100 |
Another way to get a random number | — | You choose the range: lowest and highest possible values |
| 12 | put two Dead 1010 Convert to Ten Dead |
Converts a number between bases | two, eight, Ten, 16 |
– two: binary– eight: octal– Ten: decimal– 16: hexadecimal |
| 13 | Map 50 from [0, 100] to [1, 100] |
Maps a number from one range to another | — | Useful for scaling values (e.g. sensor readings to screen size) |
🧠 Quick Tips for Students
- Use basic math blocks for scores, timing, brightness, and movement.
- Use conversion blocks when working with sensors, bytes, or number systems.
- Use random blocks for games, surprises, or unpredictable behavior.
- Use mapping when you want to turn one range of values into another (like turning 0–1023 into 0–100%).


