Communicate
Bluetooth Remote Control
🧩 Fun Guide to Bluetooth Remote Control Blocks (Clu-blocks Pro)
🎮 Important! These blocks let your robot receive commands from a phone, tablet, or another device using Bluetooth. It’s like giving your robot ears — it listens and reacts to your remote control!
| # | Block | What it does | Dropdown options | What the options mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
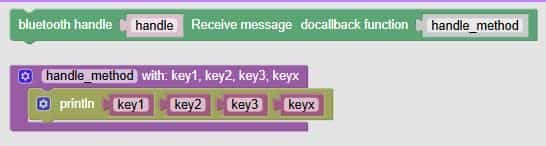
| 1 | bluetooth handle Receive message do callback function handle_method |
Sets up a listener for incoming Bluetooth messages | — | When a message arrives, it runs the handle_method function |
| 2 | handle_method with: key1, key2, key3, keyx |
Defines what to do with the received data | — | You can use these keys to control motors, LEDs, sounds, etc. |
| 3 | println key1 key2 key3 keyx |
Prints the received values | — | Great for debugging or showing what commands were received |
| 4 | if key1 = "forward" |
Checks if the command is “forward” | — | You can use conditions to trigger actions — like moving the robot |
| 5 | Bluetooth send data body "Clu-Bots" |
Sends a message back to the controller | — | Useful for confirming actions or sending sensor data |
| 6 | Whether the connection is successful |
Checks if Bluetooth is connected | — | Use this to make sure your robot is ready before reacting |
| 7 | Get local MAC address |
Gets your robot’s Bluetooth ID | — | Helpful for pairing or identifying your robot in a list |
🧠 Quick Tips for Students
- Use handle + callback to make your robot respond instantly to remote commands.
- Use key names like
"forward","left","stop"to control movement. - Use conditions to match commands and trigger actions — like turning on a motor or light.
- Use println to see what’s happening — it’s your robot’s voice for debugging.
- Always check connection status before reacting — no Bluetooth, no control!


