Blocks Area
Logic
🤔 Logic Your “Decision Maker”
What it is: Blocks that allow you to make decisions.
What it does: Answers Yes/No questions to make decisions.
Example: “If the button is pressed → turn on the LED, if not → turn it off.”
👉 It’s the thinking brain that says “yes” or “no.”
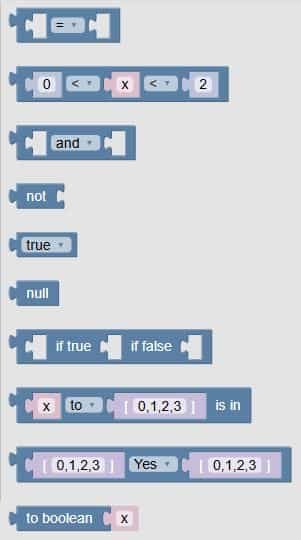
🧩 Fun Guide to Logic Blocks (Clu-blocks Pro)
🧠 Important! Logic blocks help your robot make decisions, compare things, and choose what to do next. They’re like the robot’s brain — checking if something is true or false before acting.
| # | Block | What it does | Dropdown options | What the options mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | = |
Compares two values | =, ≠, <, ≤, >, ≥ |
– =: equal– ≠: not equal– <: less than– ≤: less than or equal– >: greater than– ≥: greater than or equal |
| 2 | 0 < x < 2 |
Checks if x is between two values | <, ≤, >, ≥ |
You can build double comparisons like “between” or “outside” |
| 3 | and |
Combines two conditions | and, or, NAND, NOR |
– and: both must be true– or: at least one is true– NAND: not both– NOR: neither is true |
| 4 | not |
Flips a condition | — | If something is true, not makes it false — and vice versa |
| 5 | true |
A true/false value | true, false |
Used to test or trigger actions based on conditions |
| 6 | null |
Represents “nothing” or “empty” | — | Used when a value doesn’t exist or hasn’t been set yet |
| 7 | if true, if false |
Runs code based on a condition | — | You choose what happens when something is true or false |
| 8 | x to [0,1,2,3] is in |
Checks if a value is in a list | to, is not in |
– to: is in the list– is not in: not in the list |
| 9 | [0,1,2,3] Yes [0,1,2,3] |
Compares two lists | Yes, is not |
– Yes: lists are equal– is not: lists are different |
| 10 | to boolean x |
Converts a value to true/false | — | Turns numbers, text, or other values into a logical result |
🧠 Quick Tips for Students
- Use comparison blocks to check values (like scores, sensor readings, or time).
- Use true/false blocks to control decisions — like turning on a light only if it’s dark.
- Use list checks to see if something belongs to a group (like a password or command).
- Use logic combos (
and,or,not) to build smarter conditions.


